Description
Given a binary tree root, a node X in the tree is named good if in the path from root to X there are no nodes with a value greater than X.
Return the number of good nodes in the binary tree.
Example 1:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
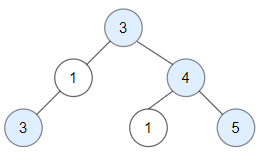
| Input: root = [3,1,4,3,null,1,5]
Output: 4
Explanation: Nodes in blue are good.
Root Node (3) is always a good node.
Node 4 -> (3,4) is the maximum value in the path starting from the root.
Node 5 -> (3,4,5) is the maximum value in the path
Node 3 -> (3,1,3) is the maximum value in the path.
|
Example 2:
1
2
3
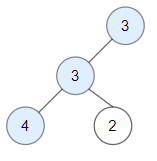
| Input: root = [3,3,null,4,2]
Output: 3
Explanation: Node 2 -> (3, 3, 2) is not good, because "3" is higher than it.
|
Example 3:
1
2
3
| Input: root = [1]
Output: 1
Explanation: Root is considered as good.
|
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the binary tree is in the range
[1, 10^5]. - Each node’s value is between
[-10^4, 10^4].
Solutions
Use DFS (depth-first traversal) , record from the root node to the current node on the path of all the nodes of the maximum value, if the value of the current node is greater than or equal to the maximum value, the current node is considered a good node, the number of plus one, finally returns the total number.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left),
* right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int goodNodes(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
dfs(root, root->val);
return num;
}
private:
void dfs(TreeNode* root, int val) {
if (root == nullptr)
return;
if (root->val >= val) {
num++;
val = root->val;
}
dfs(root->left, val);
dfs(root->right, val);
}
private:
int num{};
};
|


